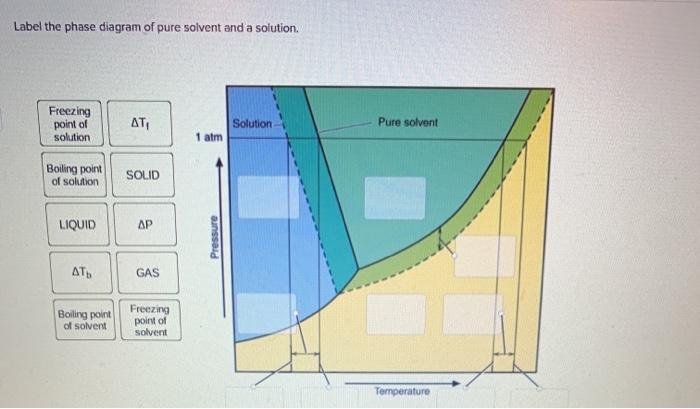
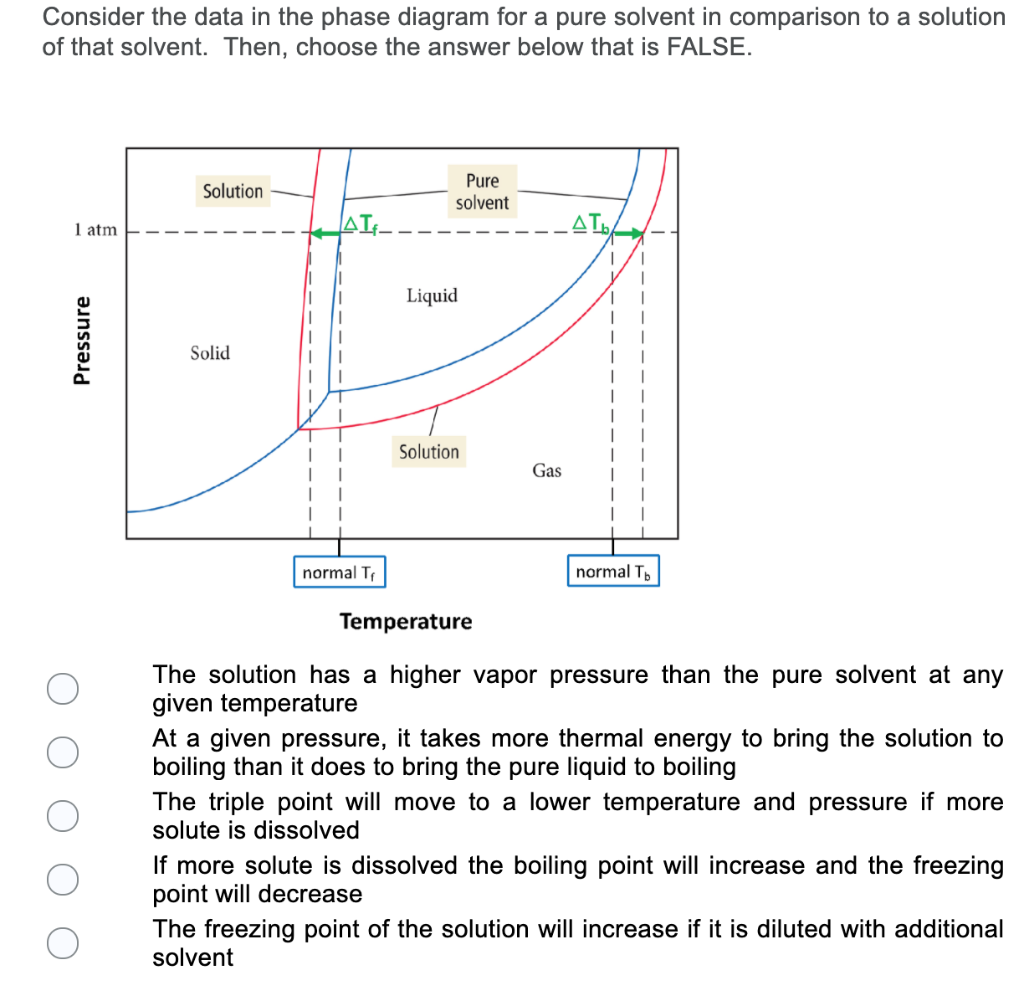
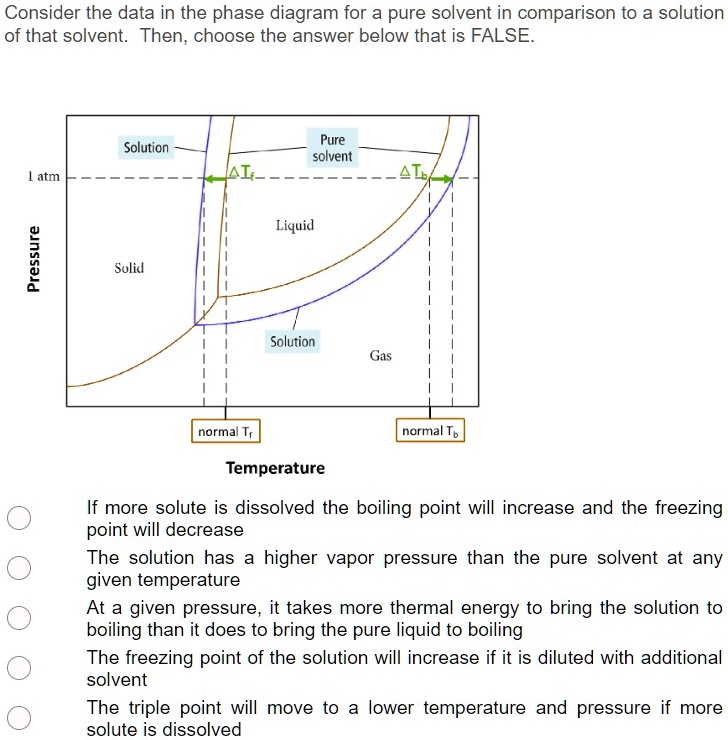
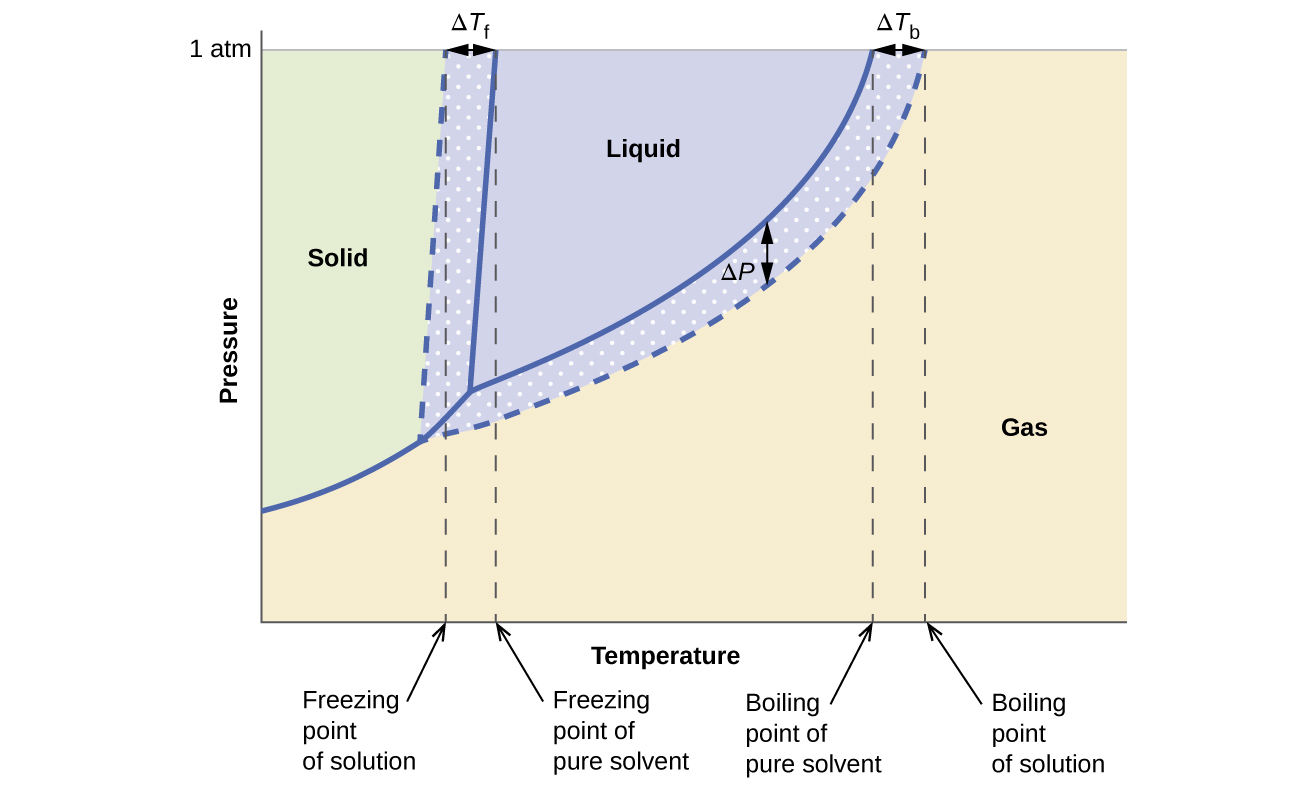
42 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
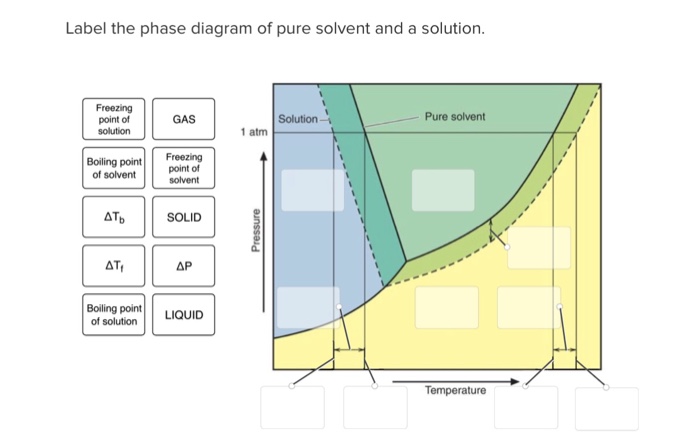
Raoult's Law and Ideal Mixtures of Liquids - Chemistry LibreTexts The partial vapor pressure of a component in a mixture is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component at that temperature multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. Raoult's Law only works for ideal mixtures. In equation form, for a mixture of liquids A and B, this reads: (1) P A = χ A P A o. (2) P B = χ B P B o. Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. - Chegg Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer
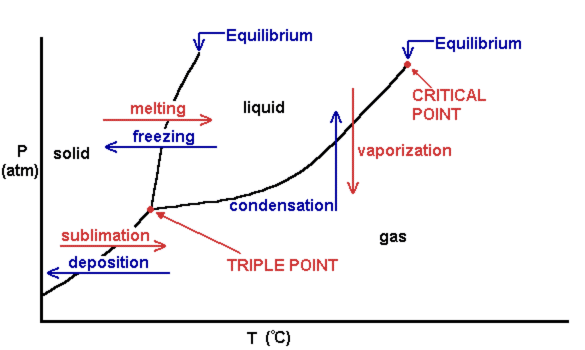
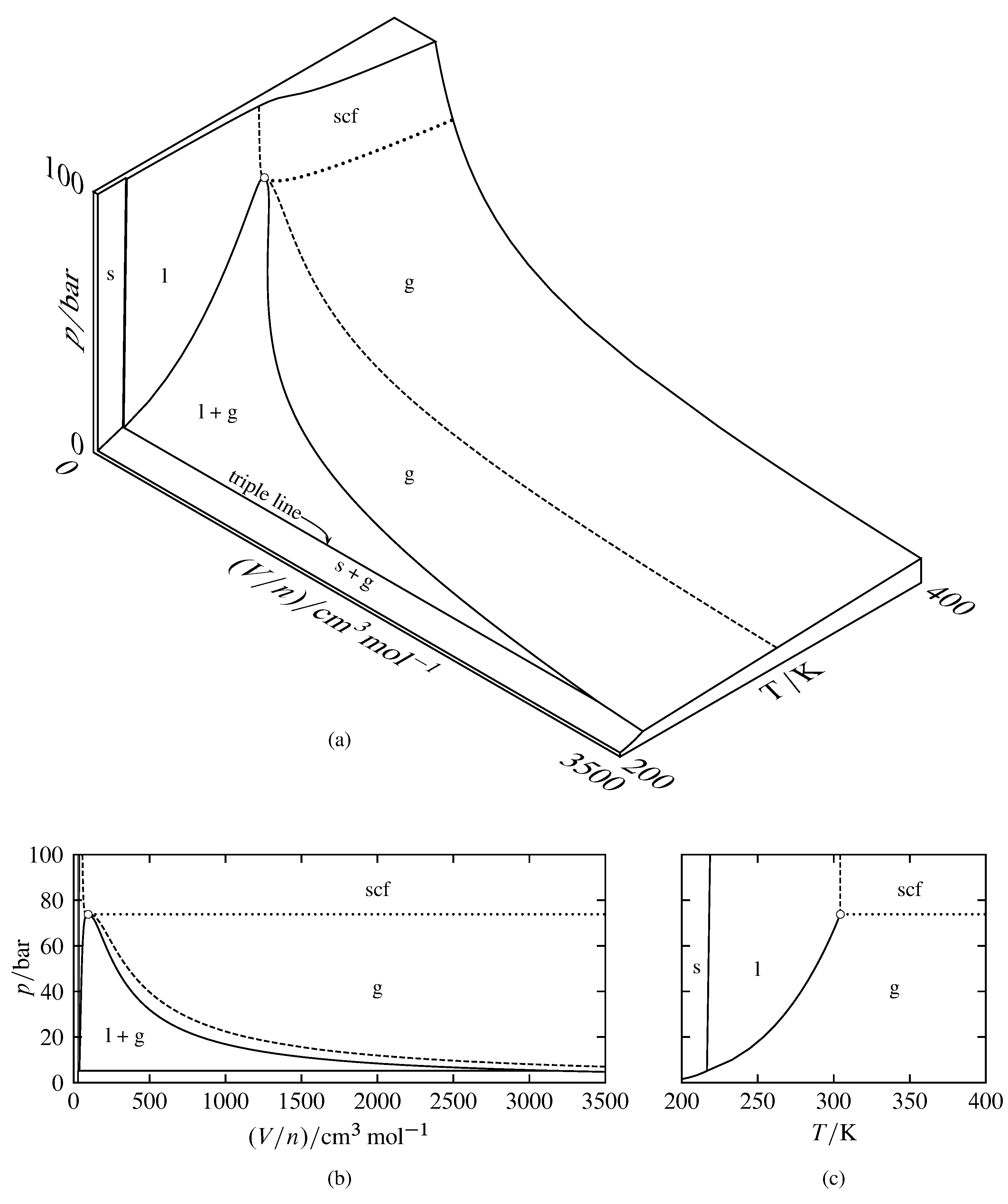
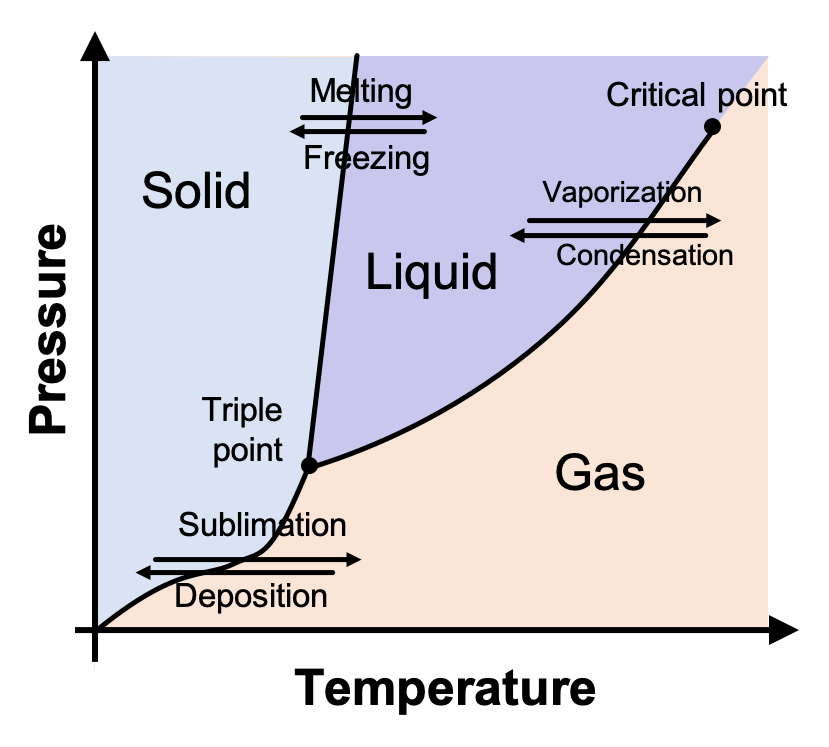
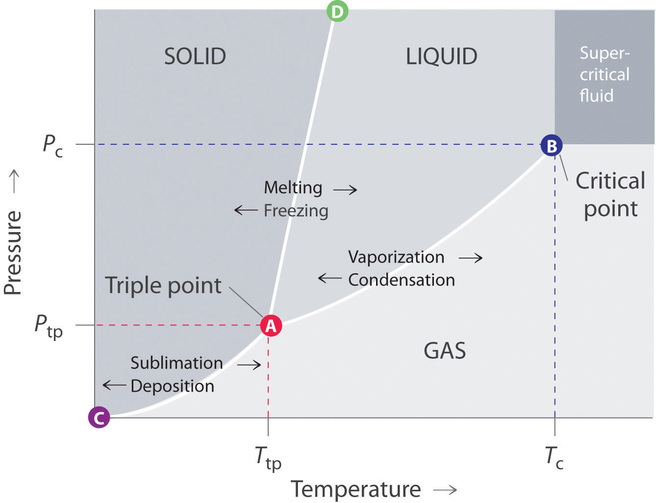
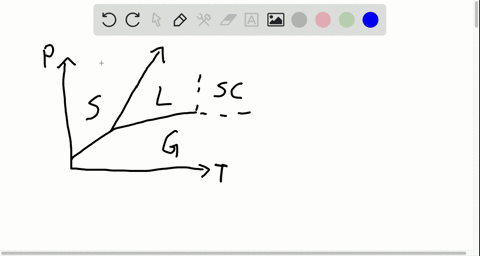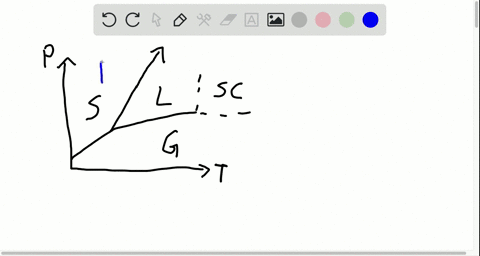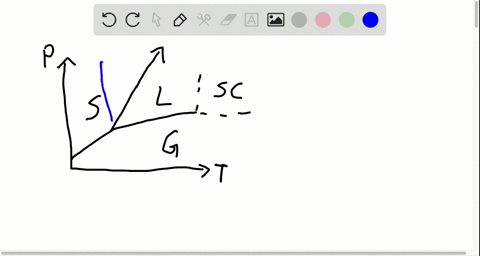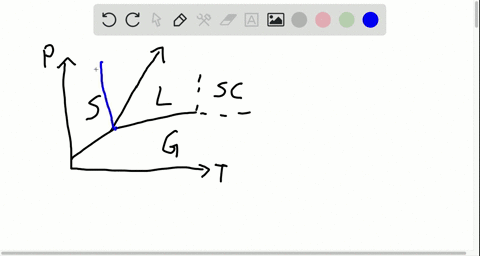
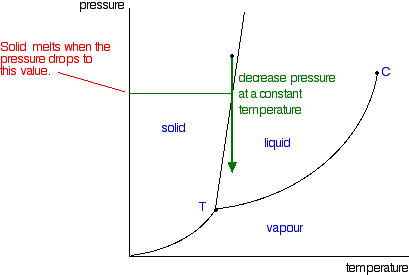
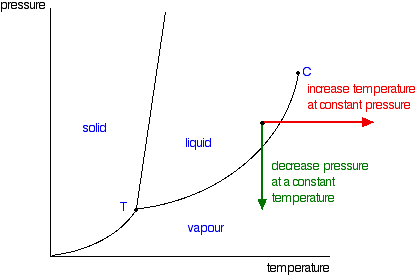
phase diagrams of pure substances - chemguide Suppose you have a pure substance at three different sets of conditions of temperature and pressure corresponding to 1, 2 and 3 in the next diagram. Under the set of conditions at 1 in the diagram, the substance would be a solid because it falls into that area of the phase diagram. At 2, it would be a liquid; and at 3, it would be a vapour (a gas).
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
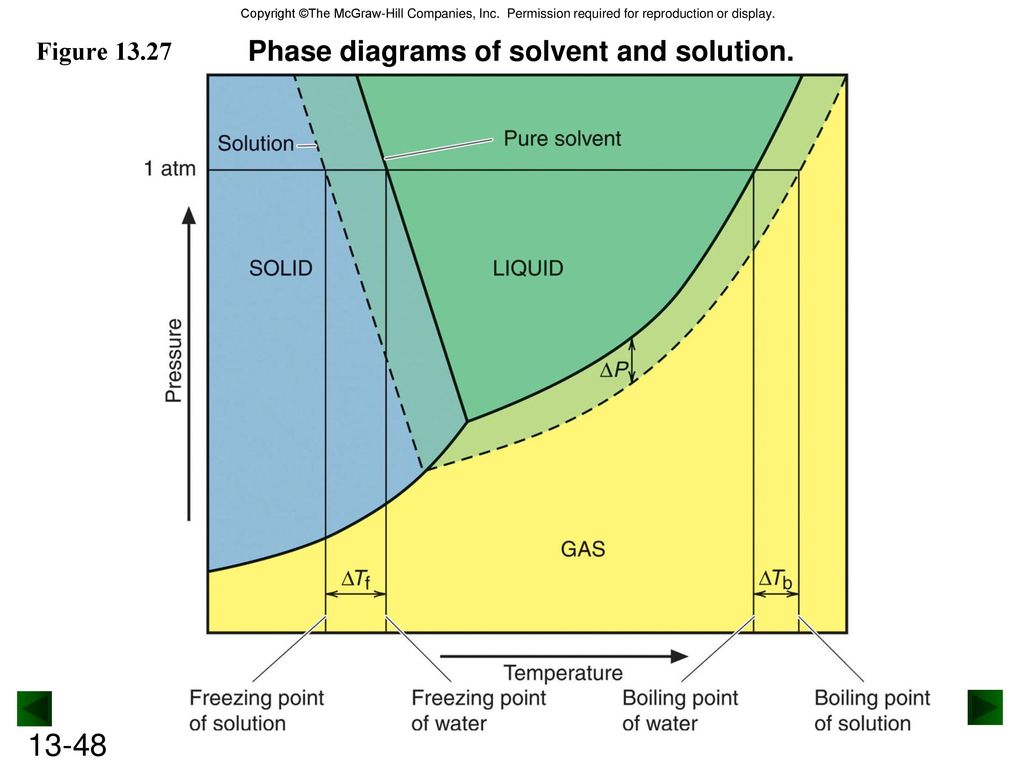
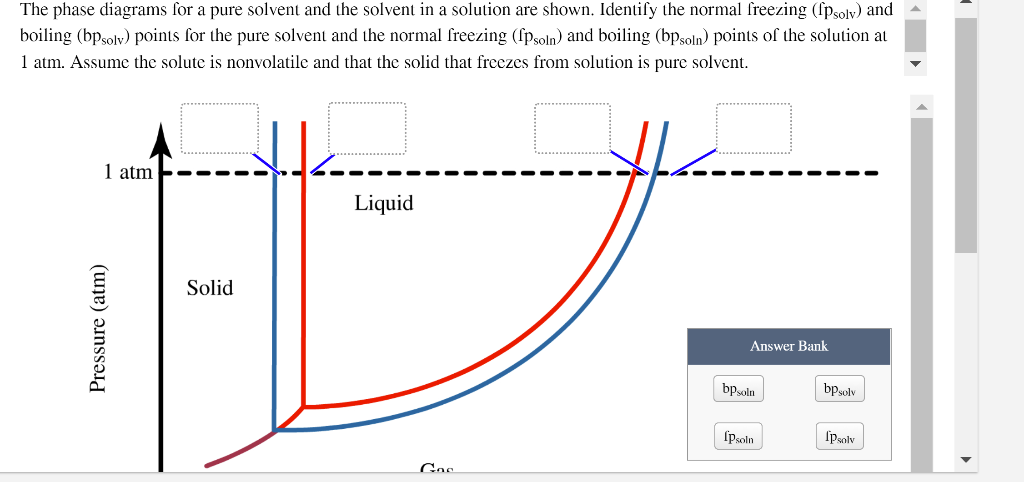
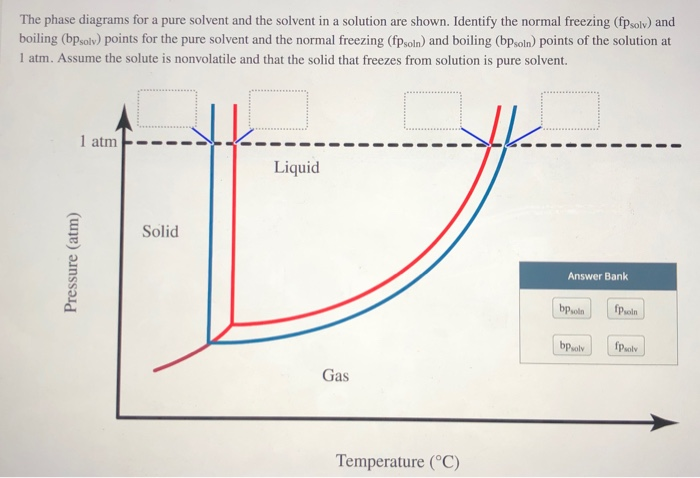
8.1: Heating Curves and Phase Changes - Chemistry LibreTexts Using the phase diagram for water, we can determine that the state of water at each temperature and pressure given are as follows: (a) solid; (b) liquid; (c) liquid; (d) gas; (e) solid; (f) gas. Exercise \PageIndex {2} What phase changes can water undergo as the temperature changes if the pressure is held at 0.3 kPa? Answered: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent… | bartleby Identify the normal freezing (fpsolv) and boiling (bpsolv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fpsoln) and boiling (bpgoln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 1 atm Liquid Solid Answer Bank fpsolv bpsolv fpsoln bpsoln Gas Temperature (°... PDF Chapter 9: Phase Diagrams - University of Washington Chapter 9 - Definitions and basic concepts • Component: pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed • System: a specific body of material under consideration • A phase: a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics • Equilibrium: a system is at equilibrium if its free energy is
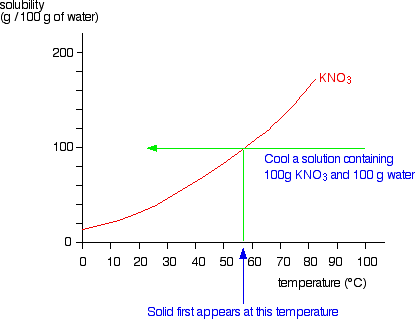
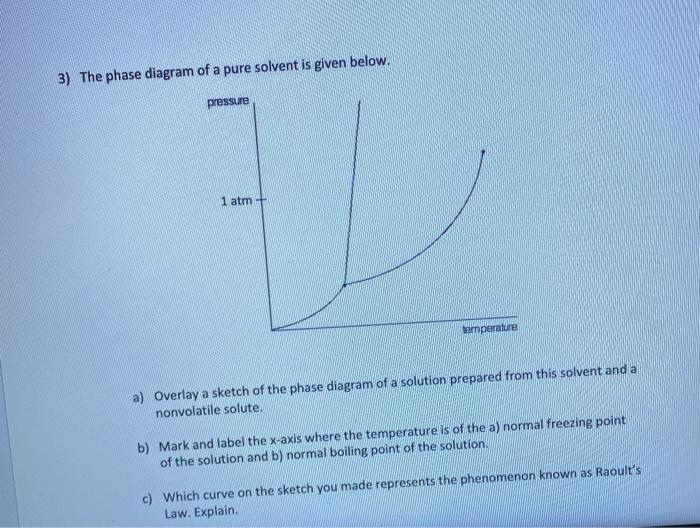
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute Doubtnut 2.5M subscribers 522 views 2 years ago The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid... Raoult's Law - Chemistry LibreTexts The diagram also includes the melting and boiling points of the pure water from the original phase diagram for pure water (black lines). Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\): Because of the changes to the phase diagram, you can see that: the boiling point of the solvent in a solution is higher than that of the pure solvent; Solved Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a - Chegg Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution Freezing point of solution GAS Solution Pure solvent 1 atm Boiling pointFreezing point of of solvent solvent ??? 11 SOLID AT AP Boiling pointLIQUID of solution Temperature This problem has been solved! Phase Diagrams for Pure Substances - Chemistry LibreTexts A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapor (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance.
[Solved] Label the phase diagram of pure solvent a | SolutionInn Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Freezing point of solution Boiling point of solvent ATb AT₁ Boiling point of solution GAS Freezing point of solvent SOLID ΔΡ LIQUID 1 atm Pressure Solution Pure solvent Temperature Expert Answer The dotted line indicates solution The linear line indicates pur View the full answer PDF phase diagram solvent solution - Just Only Effect of Solute on Phase Diagram of Water SOLID LIQUID GAS Pure solvent Freezing point of solution Freezing point of water Boiling point of water Boiling point of solution 1 atm Pressure ΔTf ΔTb ΔP Temperature. Title: phase_diagram_solvent_solution.ai Author: Joy Walker Created Date: Solved The phase diagram for a pure solvent and a dilute - Chegg The phase diagram for a pure solvent and a dilute solution of a solute are shown below. Assume the solute is nonvolatile. Identify the boiling point of the pure solvent. Previous question Next question This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Phase diagram - Wikipedia The simplest phase diagrams are pressure-temperature diagrams of a single simple substance, such as water.The axes correspond to the pressure and temperature.The phase diagram shows, in pressure-temperature space, the lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries between the three phases of solid, liquid, and gas.. The curves on the phase diagram show the points where the free energy (and other ...
Phase Diagrams - Chemistry LibreTexts Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. A typical phase diagram has pressure on the y-axis and temperature on the x-axis. As we cross the lines or curves on the phase diagram, a phase change occurs. In addition, two states of the substance coexist ... Solid solution - Wikipedia a solid solution mixes with others to form a new solution The phase diagram in the above diagram displays an alloy of two metals which forms a solid solution at all relative concentrations of the two species. In this case, the pure phase of each element is of the same crystal structure, and the similar properties of the two elements allow for ... What are the most important differences between the phase di - Quizlet For a one-component system draw a schematic labelled phase diagram given that at low T and low p, only phase γ\gammaγis present at low T and high P, only phase β\betaβis present at high T and low p, only phase α\alphaαis present; at high T and high p, only phase δ\deltaδis present: phases γ\gammaγand δ\deltaδare never in equilibrium. PDF Chapter 9: Phase Diagrams - University of Washington Chapter 9 - Definitions and basic concepts • Component: pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed • System: a specific body of material under consideration • A phase: a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics • Equilibrium: a system is at equilibrium if its free energy is
Answered: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent… | bartleby Identify the normal freezing (fpsolv) and boiling (bpsolv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fpsoln) and boiling (bpgoln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 1 atm Liquid Solid Answer Bank fpsolv bpsolv fpsoln bpsoln Gas Temperature (°...
8.1: Heating Curves and Phase Changes - Chemistry LibreTexts Using the phase diagram for water, we can determine that the state of water at each temperature and pressure given are as follows: (a) solid; (b) liquid; (c) liquid; (d) gas; (e) solid; (f) gas. Exercise \PageIndex {2} What phase changes can water undergo as the temperature changes if the pressure is held at 0.3 kPa?



















Post a Comment for "42 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution"